General information about waves
There are many forms of waves, here are some examples:
- Mechanical waves
- Needs a medium to propagate. Examples: - Ripples in water - Sound waves - Guitar string
- Electromagnetic waves
- Does not need any medium to propagate. Examples: - Light - Radio waves - X-ray
A wave can move in two different ways:
- Transversal wave
- Longitudinal wave
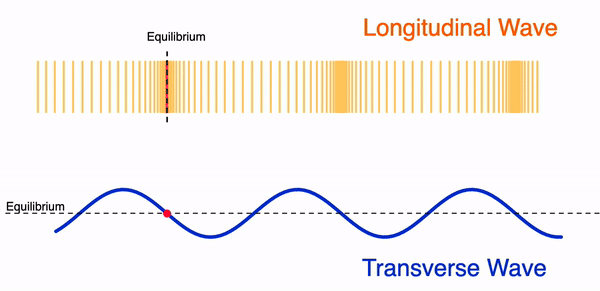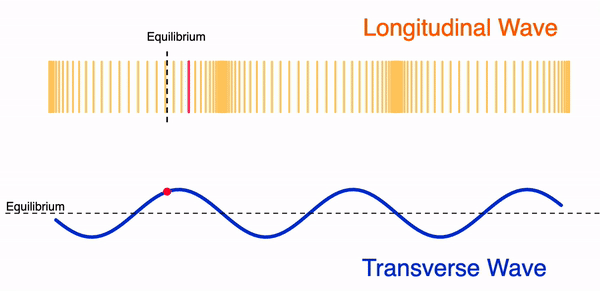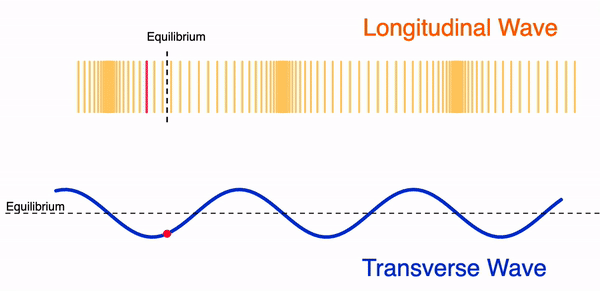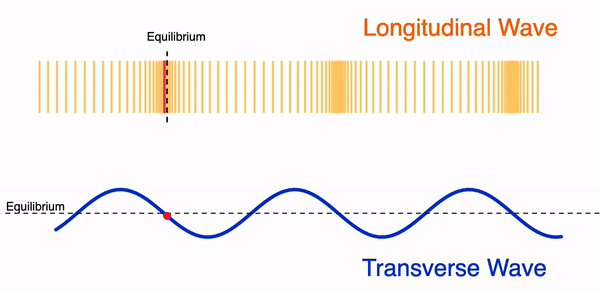
Mechanical waves can be either a transversal or a longitudinal wave. Electromagnetic waves are only found as transversal waves.
Resonance
When a system experiences resonance. Something called a standing wave will occur. A standing wave, is a wave that will change with time, but will not move in space.
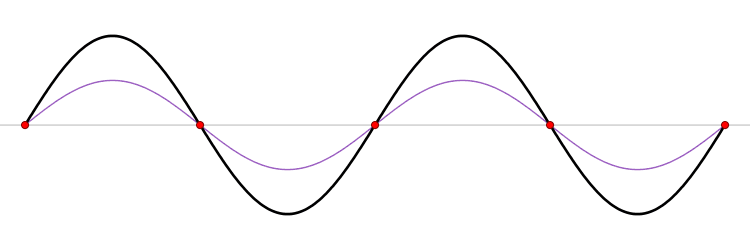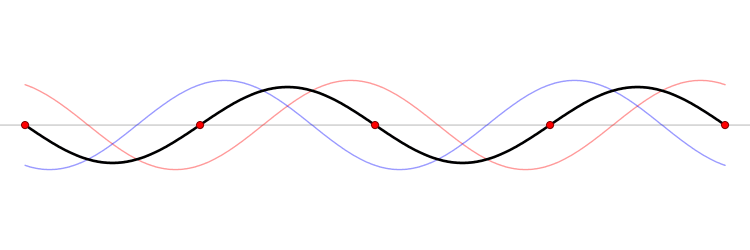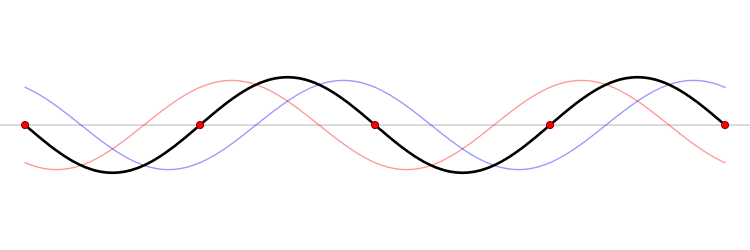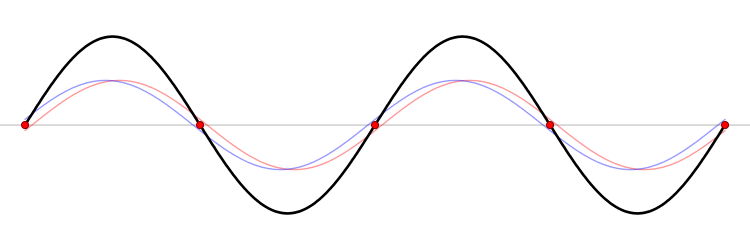
A standing wave can occur in one of two ways:
- A medium is moving in the same speed, but with opposite direction of a wave.
- For example a wave moving in the opposite direction of a river.
- Due to interference between two waves travelling the same speed in the opposite direction.
- This is the example shown in the .gif above, the black standing wave is a sum of the red and black waves.
Wave function in 1D
Derivation
bla bla bla …
Harmonic waves
Harmonic waves are a series of waves that are a integer multiple of the fundamental frequency, also known as the 1st harmonic.
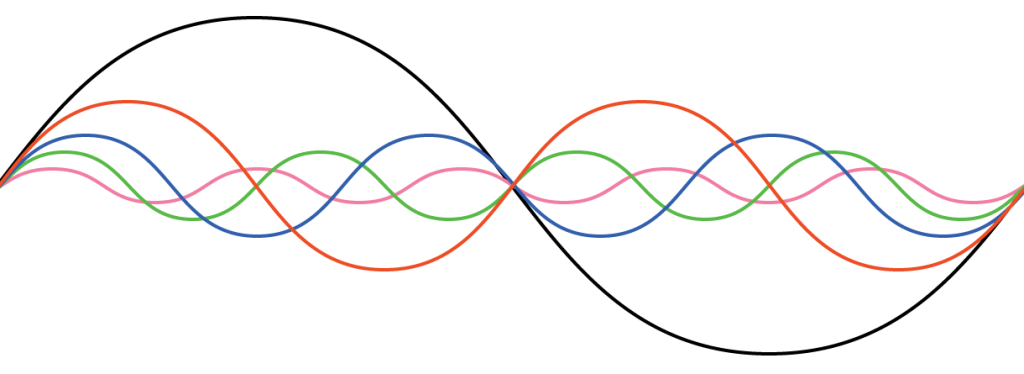
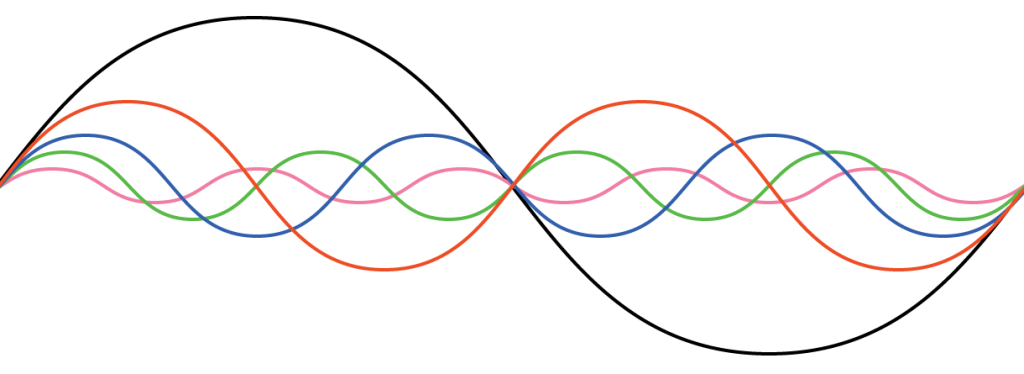
A harmonic wave satisfies the wave equation and can be given by the expression:
Where;
- is the amplitude.
- is the wave number (angular change per space).
- is the angular frequency (angular change per time).
- is the phase constant.
A harmonic wave can also be expressed in complex form.